Migrating from NRSDK to XREAL SDK
Many developers have previously created excellent applications using NRSDK (e.g., AR Lab). This guide aims to assist these developers in migrating from the original NRSDK to the new XREAL SDK, to enjoy the benefits of XRI and ARFoundation, achieving better compatibility and cross-platform functionality.
1. Prerequisites
Hardware Checklist
-
A supported Android Phone. Please review the Device Compatibility list to ensure your phone model is compatible with the glasses and XREAL SDK.
-
A pair of XREAL glasses.
-
Android Debug Bridge (adb). Wireless ADB is not required but strongly recommended, so that repetitive plug in/out can be avoided.
Software Checklist
- Unity LTS (Long Term Support) versions with Android Build Support:
If you are using Unity 2021.3.X, please use AR Foundation 5.1.0 when you need AR Features.
- XR Plugin Management
- Latest XREAL SDK for Unity
- Sample
Interaction Basics - Sample
AR Features(Optional)
- Sample
- XR Interaction Toolkit
- Sample
Starter Assets - Sample
Hands Interaction Demo(Optional)
- Sample
- AR Foundation
- XR Hands(Optional)
- Android SDK 12.0 (API Level 31) or later, installed using the SDK Manager in Android Studio
- Visual Studio (if you prefer other development environments that's fine too)
2. Import XRI and AR Foundation
-
Install XR Interaction Toolkit from the Unity Registry in the Package Manager and import Starter Assets in Samples tab.
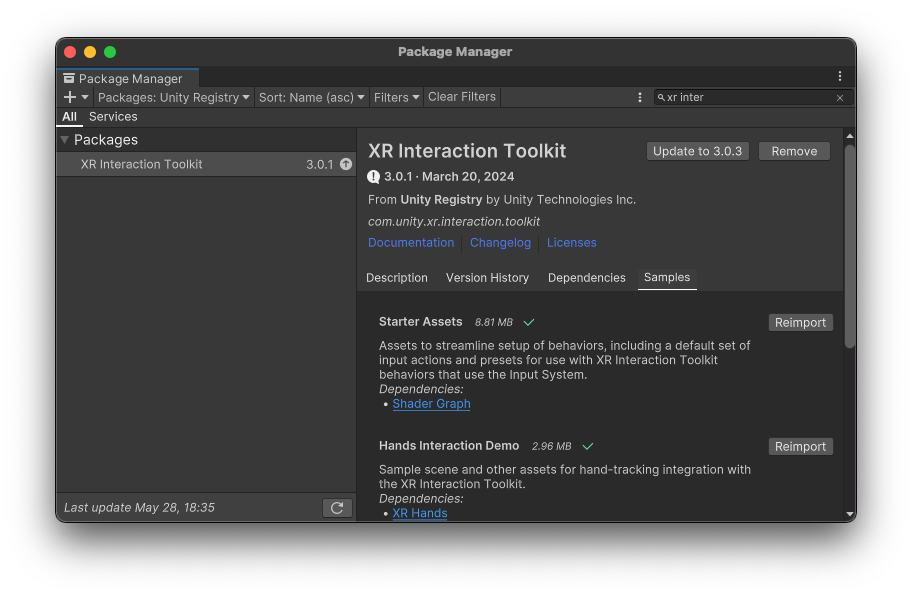
There will be a warning about new input system, and requires you to restart the editor, just click yes.
-
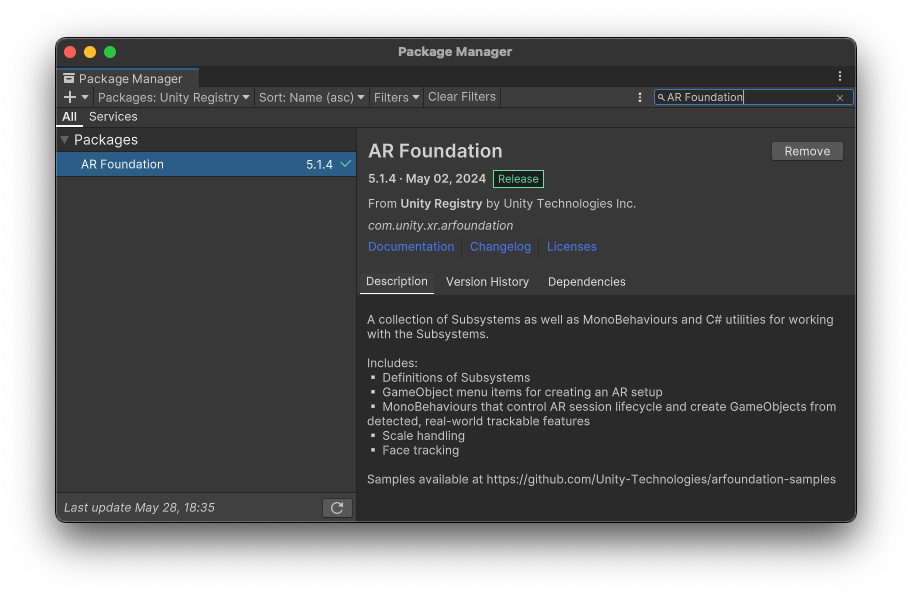
Install AR Foundation from the Unity Registry in the Package Manager.
3. Import XREAL SDK for Unity
Open Window -> Package Manager,
- Add pacakge from tarball
When importing the XREAL SDK into your Unity project, you'll encounter several key components that facilitate the development of AR applications. Here's a breakdown of the essential and optional elements:
-
Interaction Basics: This is an essential component that provides assets to streamline the setup of basic rendering and interactions using controllers and hand gestures, compatible with the XR Interaction Toolkit. It includes prefabs and demo scenes designed to help you get started quickly with the XREAL SDK integration. This component is fundamental as it lays the groundwork for any XR application, ensuring that you have the necessary tools for basic interaction and rendering.
-
AR Features: This is an optional component, recommended for those who require advanced AR functionalities in their projects. It includes sample scenes and other assets that demonstrate the integration of AR features supported by the XREAL SDK with AR Foundation. This part specifically supports Plane Detection, Image Tracking, Spatial Anchors, and Depth Meshing. Depending on the scope of your project, you can choose to import this component if your application will utilize complex AR features.
When setting up your project, start with the Interaction Basics to ensure all fundamental interaction mechanisms are in place. Then, depending on the AR features necessary for your project, consider importing the AR Features module to expand the application's capabilities with advanced AR technology. This modular approach allows you to keep your project lightweight by only including the components necessary for your specific needs.
4. Configure Project Settings
You could either configure your project automatically via XREAL SDK Project Setup tool or configure manually. These two ways are equivalent.
Project Setup Tool
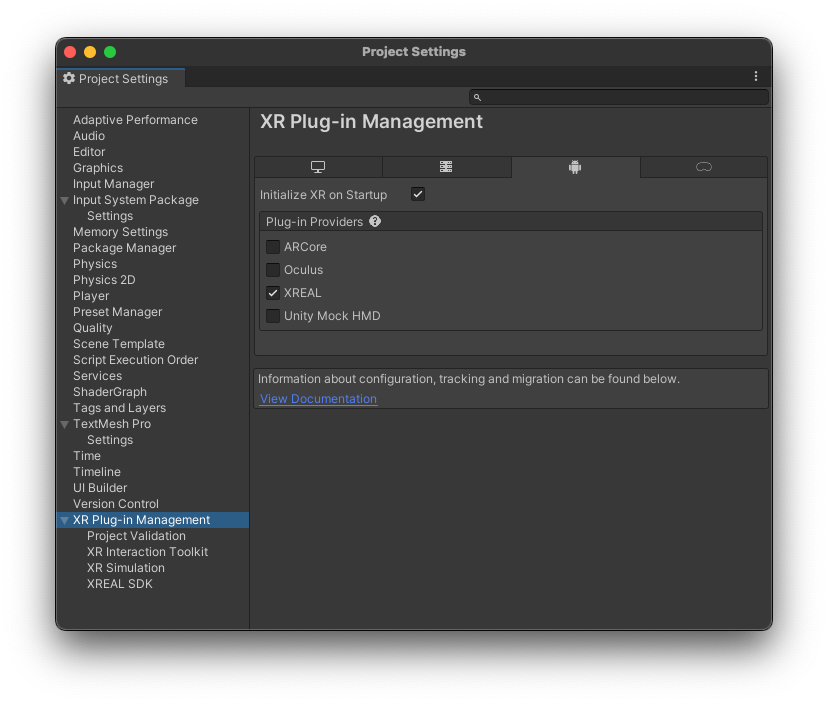
- To enable XREAL XR Plug-in, navigate to the project settings under Edit > Project Settings > XR Plug-in Management and open the Android tab. Check the XREAL plug-in.
- Initially, there might be some project settings that have to be updated/fixed. To do so, go to
Project Validationwindow. Click on the fix buttons next to the entries to apply the needed project settings.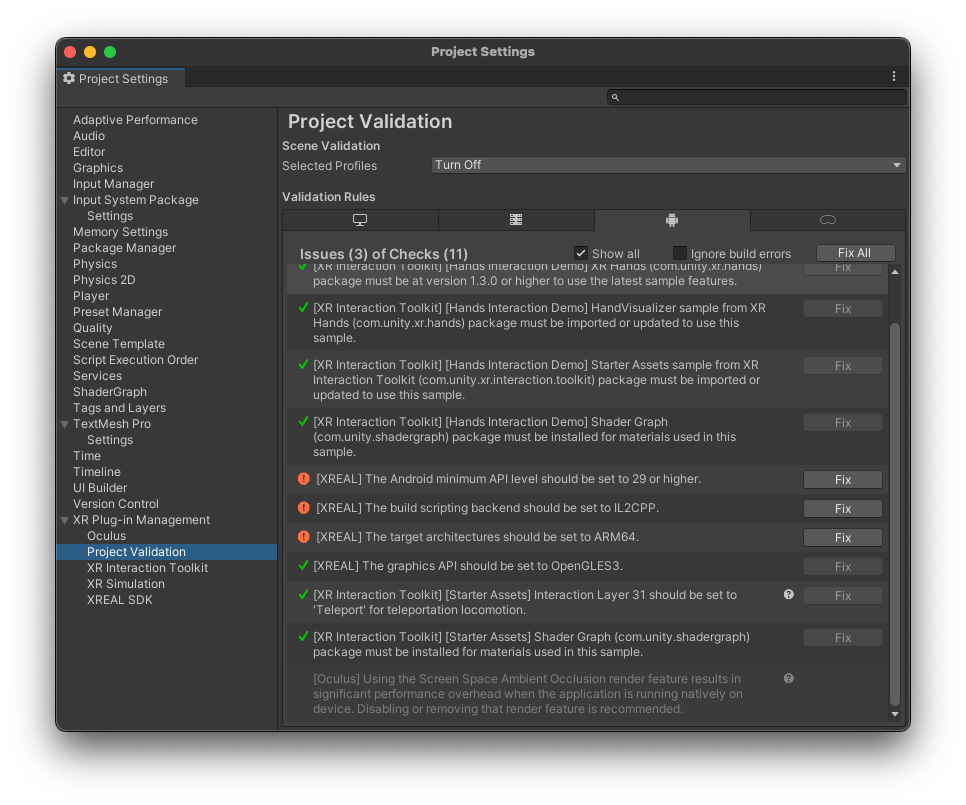
Manual Configuration
-
Go to File > Build Settings.
-
Select Android and click Switch Platform.
-
In the Build Settings window, click Player Settings.
-
In the Inspector window, configure player settings as follows:
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
Player Settings > Resolution and Presentation > Default Orientation | Portrait |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Auto Graphics API | false |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Graphics APIs | OpenGL ES3 |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Package Name | Create a unique app ID using a Java package name format. For example, use com.xreal.helloMR |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Minimum API Level | Android 10.0 or higher |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Target API Level | Automatic (highest installed) |
Player Settings > Other Settings > Write Permission | External(SDCard) |
Project Settings > Quality > VSync Count | Don't Sync |
XREAL Specific Settings
In this section, we outline the key project settings available in the XREAL SDK, which allow developers to configure various aspects of stereo rendering, tracking, input sources, and device compatibility to optimize their AR applications for specific use cases.
Access these settings via Edit > Project Settings > XR Plug-in Management > XREAL:
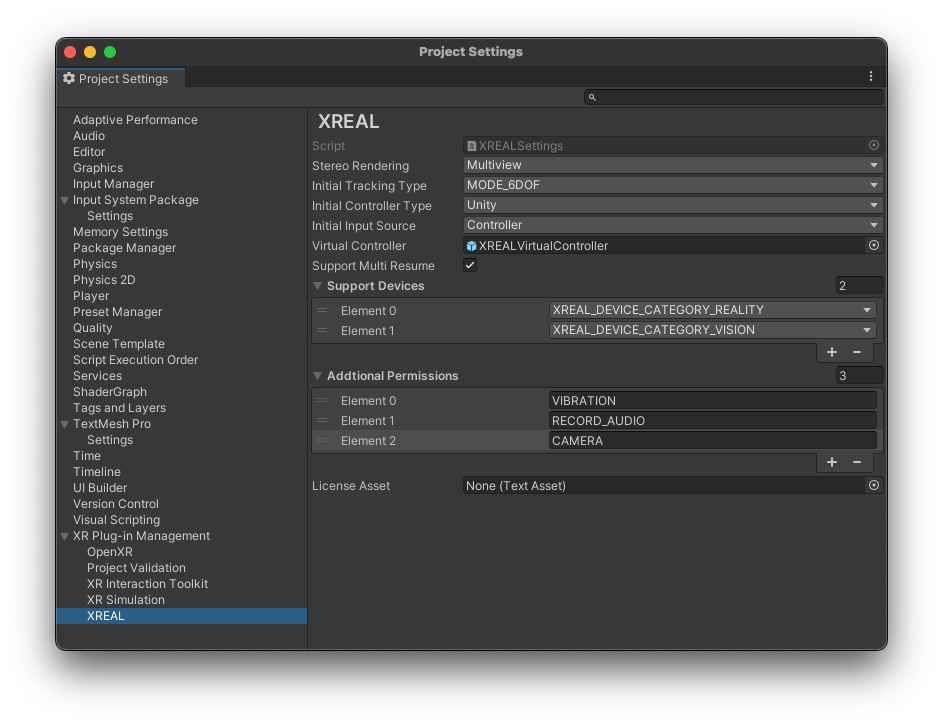
-
Stereo Rendering Mode- Multi-view (Recommended): This mode renders the left and right eye views in a single pass, reducing the overhead and potentially increasing performance.
- Multi-pass: In this mode, the left and right eye views are rendered in separate passes, which can be less efficient but may be necessary for certain effects or compatibility.
-
Initial Tracking Type- MODE_6DOF (Recommended for XREAL Air 2 Ultra): Allows tracking of both position and rotation in 3D space, providing a fully immersive experience.
- MODE_3DOF (Recommended for XREAL Air/Air 2): Tracks only rotational movement, meaning the user can look around but not move within the space.
- MODE_0DOF: No tracking of movement or rotation.
- MODE_0DOF-STAB: No tracking but ensures a stable view, using some form of sensor data to reduce drift.
-
Initial Input Source- Hands: Uses hand tracking for input.
- Controller: Uses BeamPro or an Android phone as a controller for input.
- None: No input source is used.
-
Virtual Controller: XREAL SDK allows the use of external devices, like BeamPro or Android phones, as virtual controllers. This setting defines the layout and functionality of the on-screen buttons for these controllers. -
Support Multi Resume(Recommended: Enabled) Enables dual-screen independent display mode, allowing the AR app to continue displaying in the glasses while the phone screen can switch to other 2D apps. When enabled:- The AR view remains active in the glasses even when the app is in background
- Users can freely use other apps on their phone screen
- Requires user permission on first launch
- Enabled by default in XREAL Settings

For more detailed information about dual-screen display, see Dual Screen Display.
-
Support Devices(Recommended: Enable both categories for maximum compatibility)- XREAL_DEVICE_CATEGORY_REALITY: Glasses with 6DoF tracking capabilities, such as the XREAL Air 2 Ultra.
- XREAL_DEVICE_CATEGORY_VISION: Glasses with 3DoF tracking capabilities, such as the XREAL Air 2 and XREAL One Series.
-
Android Permissions(Enable as needed for your app's functionality) Android permissions can be incorporated either by modifying the general Android Manifest.xml file or by utilizing the XREAL Settings interface for a more streamlined approach.- VIBRATION: Required for haptic feedback.
- CAMERA: Required for RGB camera access and recording.
- AUDIO: Required for audio recording features.
5. Basic Migration Steps
5.1 Remove NRSDK Components
- Duplicate any custom assets from NRSDK you need into another folder
- Delete the NRSDK folder from Assets
- Replace NRCameraRig with XR Interaction Setup prefab or XR Interaction Hands Setup prefab
- Remove NRInput from Hierarchy
- Add AR Session to Hierarchy
5.2 Building and Deployment
-
Access the Build Settings in Menu -> File -> Build Settings. Click the button "
Add Open Scene" and make sure the current scene is checked.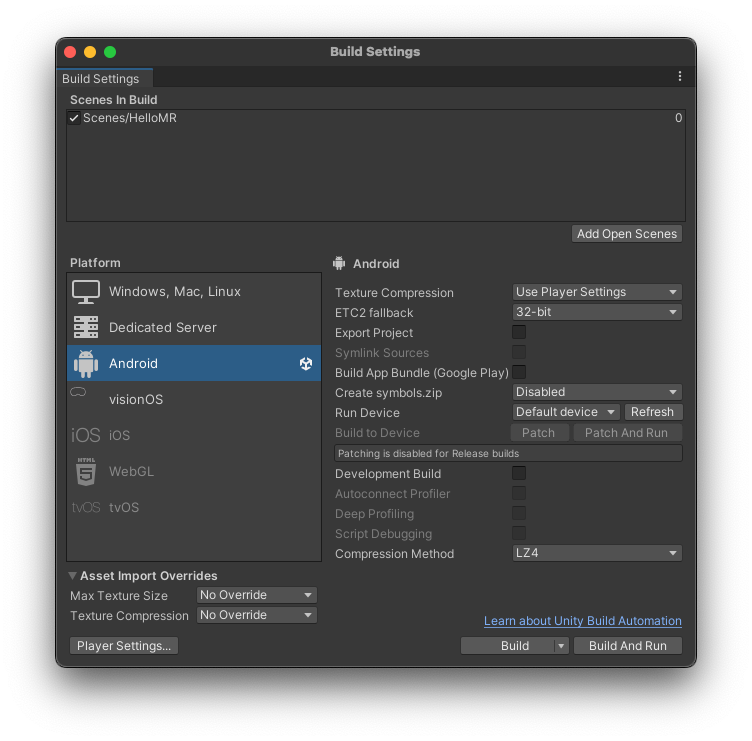
-
Click Player Settings. Customize the Company Name and Product Name.
-
(Optional) Navigate to the Android> Other Settings panel to specify your build settings. As you have prepared. You may leave the current configuration as it is. It is worth noting some of the other settings:
-
Multithreaded Rendering: Enable this option to use multithreaded rendering. In most cases, both enabling and disabling this option is supported by XREAL SDK. However, for the scenes that contains Overlay content, you should disable multithreaded rendering. And When developing URP projects, if single pass rendering is not used, it is best to also turn off Multithreaded rendering, otherwise tearing may occur.
-
Scripting Backend: You must choose IL2CPP when building for ARM64 architecture. Note that starting from NRSDK 2.2, ARMv7 architecture is no longer supported.
-
In Build Settings window, click Build.
-
Select the destination folder and wait until the building is finished.
-
Connect your Phone / Beam Pro to your Mac / Windows PC.
-
Install your app through WiFi Android Debug Bridge (adb) or type-C cable after the build is successful.
-
Disconnect the device with your PC, and then connect it to the glasses.
-
Open ControlGlasses(Android phone) or MyGlasses(Beam Pro), then find your app then click to open it.
-
Grant the necessary permissions if prompted, especially ensure that "Allow to display over other apps" is checked.
-
(Optional) Use Android Logcat to view logged messages. We recommend using WiFi Android Debug Bridge (adb) to connect to your PC so that you do not have to be connected through the data cable most of the time.
-
Enable developer options and USB debugging on your Phone / Beam Pro. Android Debug Bridge (adb) is enabled as default and does not require manual setting.
6. API Migration Reference
To help developers migrate their existing NRSDK applications to XREAL SDK, here's a comprehensive reference table of API changes. This table lists all the important changes in class names, APIs, callbacks, and configurations.
6.1 Namespace/Class Name Renaming
| Old Name | New Name |
|---|---|
| NRVideoCapture | XREALVideoCapture |
| NRDeviceType | XREALDeviceType |
| NRPhotoCapture | XREALPhotoCapture |
| NRCaptureBehaviour | XREALCaptureBehaviour |
| NRCameraInitializer | XREALCameraInitializer |
| NativeDevice | XREALComponent |
| ControllerButton | XREALControllerButton |
| NRAndroidPermissionsManager | XREALAndroidPermissionsManager |
| NRPointerRaycaster | UnityEngine.EventSystems.PointerEventData or UnityEngine.XR.Interaction.Toolkit.XRRayInteractor |
| CanvasRaycastTarget | TrackedDeviceGraphicRaycaster |
6.2 API Changes
| Old Interface | New Interface |
|---|---|
| MainThreadDispather.QueueOnMainThread | XREALMainThreadDispather.QueueOnMainThread |
| NRSessionManager.Instance.NRHMDPoseTracker.ChangeTo3Dof | XREALPlugin.SwitchTrackingTypeAsync() |
| NRDevice.Subsystem.GetDeviceType() | XREALPlugin.GetDeviceType() |
| NRDevice.Subsystem.AddEventListener | XREALPlugin.RegisterKeyEventCallback |
| NRDevice.Subsystem.GetElectrochromicLevel | XREALPlugin.GetElectrochromicLevel |
| NRFrame.targetFrameRate | XREALPlugin.SetTargetFrameRate |
| NRFrame.MonoMode | XREALPlugin.Get2D3DMode |
| NRSessionManager.Instance.IsRunning | XREALUtility.GetLoadedSubsystem<XRSessionSubsystem>().running |
6.3 Callback System Changes
| Old Callback | New Callback |
|---|---|
| NRSessionManager.OnGlassesStateChanged | XREALPlugin.RegisterGlassesWearingCallback, XREALCallbackHandler.OnXREALGlassesWearingState |
| NRDevice.OnSessionSpecialEvent | XREALXRLoader.OnStartDisplaySubsystem, OnStartInputSubsystem |
| NRSessionManager.OnKernalError | XREALNativeCallbackHandler.NativeErrorCallback |
| NRGlassesInitErrorTip.OnPreComfirm | XREALErrorReceiver.OnXREALSDKFailPreComfirm |
6.4 Configuration Changes
| Old Configuration | New Configuration |
|---|---|
| NRSessionManager.Instance.NRSessionBehaviour.SessionConfig.SupportMultiResume | XREALSettings.GetSettings().SupportMultiResume |
| NROverlay related components | Use Composition Layers from the XREAL XR Plugin Samples |
| IPoseProvider | Unity.XR.XREAL.Examples.IDataSource |
6.5 Special Handling Instructions
- Singleton Pattern Changes:
- For singletons that do not inherit from MonoBehaviour, use Unity.XR.XREAL.Singleton.
- For singletons that inherit from MonoBehaviour, use Unity.XR.XREAL.SingletonMonoBehaviour.
- Performance Optimization:
- QualitySettings.antiAliasing should be set before NRSwapChainManager::CreateTexture.
- This can be set in the XREALXRLoader.OnStartInputSubsystem or XREALXRLoader.OnXRLoaderStart callbacks.
- Editor Related:
- Import the XR Device Simulator from the XR Interaction Toolkit.
- The GraphicRaycaster on the Canvas may affect event handling in editor mode.
6.6 NRInput Migration
When migrating from NRInput, you have two options:
Option 1: Migrate to XR Interaction Toolkit Input Actions (Recommended)
This approach aligns with modern XR development practices and provides better compatibility with other XR platforms. Here's how to migrate:
- Replace NRInput button checks with Input Actions:
// Old NRInput code
if (NRInput.GetButtonDown(ControllerButton.TRIGGER)) {
// Handle trigger press
}
// New Input Action code
[SerializeField]
private InputActionProperty m_TriggerAction;
private void OnEnable() {
m_TriggerAction.action.performed += OnTriggerPressed;
}
private void OnTriggerPressed(InputAction.CallbackContext context) {
// Handle trigger press
}
- Replace controller state queries:
// Old NRInput code
Vector3 position = NRInput.GetPosition();
Quaternion rotation = NRInput.GetRotation();
// New Input System code
public XRController controller;
void Update() {
if (controller.inputDevice.TryGetFeatureValue(CommonUsages.devicePosition, out Vector3 position)) {
// Use position
}
if (controller.inputDevice.TryGetFeatureValue(CommonUsages.deviceRotation, out Quaternion rotation)) {
// Use rotation
}
}
- Replace haptic feedback:
// Old NRInput code
NRInput.TriggerHapticVibration(duration, amplitude);
// New Input System code
public XRController controller;
void TriggerHaptic() {
controller.SendHapticImpulse(0, amplitude, duration);
}
Option 2: Use XREALInput Compatibility Layer
If you prefer to maintain code similarity with your existing NRInput implementation, you can use the XREALInput class which provides a similar API:
- Add the XREALInput script to your project and update your namespace references:
// Old code
using NRInput;
// New code
using Unity.XR.XREAL.Samples;
- Replace NRInput calls with XREALInput:
// Old code
if (NRInput.GetButtonDown(ControllerButton.TRIGGER)) { }
Vector3 position = NRInput.GetPosition();
NRInput.TriggerHapticVibration(duration, amplitude);
// New code
if (XREALInput.GetButtonDown(ControllerButton.TRIGGER)) { }
Vector3 position = XREALInput.GetPosition();
XREALInput.TriggerHapticVibration(duration, amplitude);
The XREALInput class maintains similar method signatures and functionality to NRInput while using the new input system internally. This can be a good intermediate step if you want to gradually transition to the new input system.
Key differences to note:
- The XREALInput class uses Unity's new Input System internally
- Some advanced features may have slightly different implementations
- The class is provided in the Samples namespace as a migration aid
Choose the migration approach that best fits your project's needs:
- Option 1 if you're starting a new project or want to fully embrace the new input system
- Option 2 if you want to minimize code changes while still upgrading to the new SDK
7. Feature-Specific Migration Guides
For detailed migration instructions for specific AR features, please refer to: